Focus on biodiversity: Links between the flow of rivers and diversity of fish species
Published: April 30, 2014
There is increasing concern about the global decline of biodiversity. In particular, changes in the flow of rivers due to climate change and increasing water consumption affect freshwater biodiversity including fish species richness (FSR).
However, due to limited ecological data and immaturity of flow indices, the link between the flow of rivers and FSR on a global scale is unclear.
Here, Chihiro Yoshimura and his colleagues in Department of Civil Engineering have developed empirical models to relate FSR to several flow indices and other parameters of rivers on a global scale.
Flow regime of rivers was assessed by ecologically important indices and then statistically linked to FSR data using a generalized linear model, which enables scenario analysis for the future.
The results of the model have provided the first empirical indication that specific low and high flow characteristics of rivers may be important in explaining variations in basin-scale FSR.
These findings may be useful in identifying high-risk basins in terms of the conservation of fish species diversity. In ongoing work, other factors, for example dams and fish traits, are being incorporated into the FSR model.
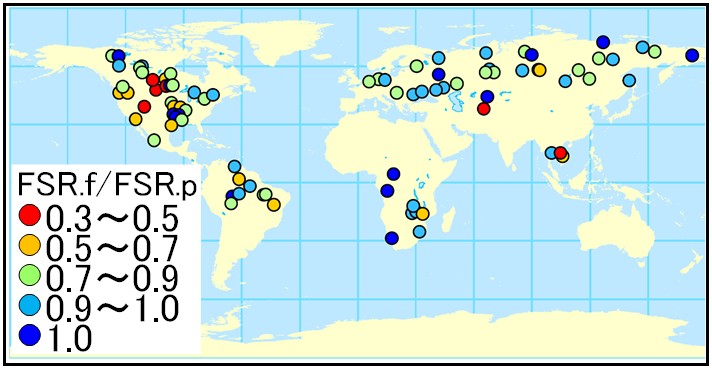
Fig. Ratio of potential species richness of native fish in the future (2036-2050, FSR.f) compared to the past (1971-1985, FSR.p) in each basin under a scenario of enhanced irrigation and climate change.
Reference:
Authors: |
Yuichi IWASAKI, Masahiro RYO, Pengzhe SUI, and Chihiro YOSHIMURA |
Title of original paper: |
Evaluating the relationship between basin-scale fish species richness and ecologically relevant flow characteristics in rivers worldwide |
Journal volume, pages and year: |
Freshwater Biology 57(10), 2173-2180 (2012) |
Digital Object Identifier (DOI): |
|
Affiliations: |
Department of Civil Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology, |
. Any information published on this site will be valid in relation to Science Tokyo.



