E-cad-Fc: A nanobiomachine that could help in rebuilding damaged livers
It has recently been shown that natural extracellular matrices (ECMs) – the parts of animal tissue that provide structural support to the cells – can be combined with culture media to aid the proliferation and differentiation of embryonic stem (ES) cells into liver cells, such as hepatocytes. However, the natural substrates used to provide ECM are undefined, generate a complex environment, and can place considerable stress on the differentiating cells during culture.
Now, researchers at Tokyo Tech's Department of Biomolecular Engineering, under the supervision of Toshihiro Akaike, have developed a new engineered ECM using a recombinant E-cadherin extracellular domain fused to an Fc region of immunoglobin G, abbreviated as E-cad-Fc. This engineered ECM can specifically support the efficient proliferation and differentiation of mouse ES cells into hepatocytes.
This new scheme of hepatocyte differentiation requires three steps. Firstly, the undifferentiated ES cells are cultured in the presence of a cytokine called LIF, before inducing their differentiation to endodermal cells in presence of the growth factor complex Activin A and bFGF. Finally, they are induced to differentiate into mature hepatocytes by adding hormones and growth factors related to liver development.
In contrast to conventional ECMs, such as a gelatin-coated plate, all the differentiated cells on the E-cad-Fc immobilized matrix formed a scattered distribution, and showed evidence of efficient expression of endoderm markers. Moreover, the final stage showed enhanced expression of early and late hepatocyte markers, such as α-fetoprotein, albumin, ASGP-R and the storage of glycogen.
E-cad-Fc could find widespread applications as nanobiomaterials for the large-scale production of hepatocytes under 3-D culture conditions.
Reference
M.A. Haque, M. Nagaoka, B. Hexig & T. Akaike. Artificial extracellular matrix for embryonic stem cell culture: a new frontier of nanobiomaterials. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials 11, 014106 (2010).
M. Nagaoka, Y. Hagiwara, K. Takemura, Y. Murakami, J. Li, S.A. Duncan & T. Akaike. Design of the artificial acellular feeder layer for the efficient propagation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry 283, 26468-26476 (2008).
M. Nagaoka, U. Koshimizu, S. Yuasa, F. Hattori, H. Chen, T. Tanaka, M. Okabe, K. Fukuda & T. Akaike. E-cadherin-coated plates maintain pluripotent ES cells without colony formation PLoS One 1, e15 (2006).
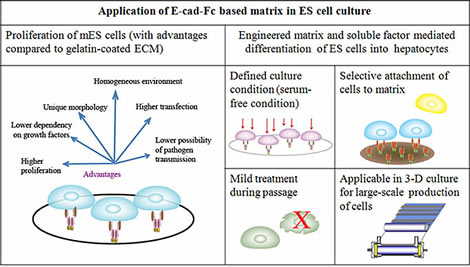
Applications of the recombinant E-cad-Fc matrix which promotes
embryonic stem cells to proliferate and differentiate into liver cells.
. Any information published on this site will be valid in relation to Science Tokyo.



