Evacuation procedures in big cities after massive earthquakes: Models based on the behavior of people in Tokyo after the Tohoku-Pacific Ocean Earthquake on 11 March 2011
The Tohoku-Pacific Ocean Earthquake occurred on 11 May 2011. On this day all rail services in the Tokyo Metropolitan area were paralyzed amid the unprecedented confusion that followed the tremor.
Thousands people were unable to contact families and friends, and in a state of uneasiness, many decided to return home on foot. Main roads were heavily congested with both cars and people, a state which severely obstructed the movement of emergency vehicles.
Here, Toshihiro Osaragi at Tokyo Institute of Technology describes the construction of several models that describe decision-making and behavior of individuals attempting to reach home on foot in the wake of a devastating earthquake.
He has simulated the movement of individuals who have decided to return home on foot, and demonstrates the spatiotemporal distribution of those who might be exposed to hazardous city fires on their way home in the aftermath of a massive earthquake, which has been predicted to occur in the Tokyo Metropolitan area in near future.
Osaragi research underscores the importance of considering pedestrian flow under such extreme scenarios in order to establish emergency evacuation procedures. "Using the model proposed, we can assess not only the potential number of stranded individuals, but also their detailed attributes," says Osaragi. "Such information would undoubtedly prove helpful in actual planning for immediate post-disaster mitigation."
Reference
- Authors: Toshihiro Osaragi.
- Title of original paper: Modeling a spatiotemporal distribution of stranded people returning home on foot in the aftermath of a large-scale earthquake.
- Journal, volume, pages and year: Natural Hazards, Springer, (2012).
- Digital Object Identifier (DOI): 10.1007/s11069-012-0175-8
- Affiliations: Department of Mechanical and Environmental Informatics, Graduate School of Information Science and Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology.
- Department website: osaragi@mei.titech.ac.jp
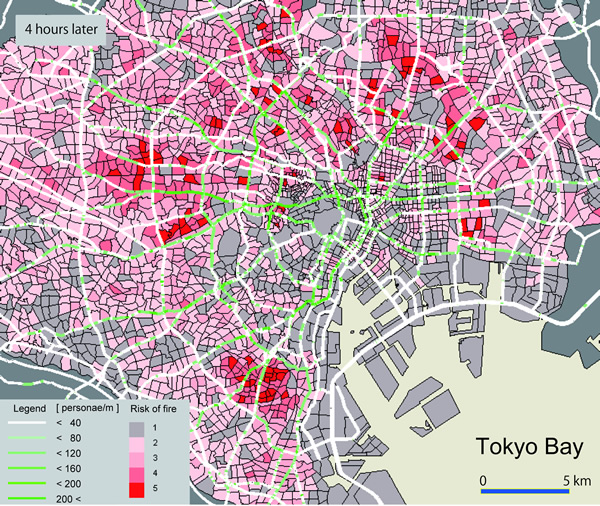
Risk of fire and spatiotemporal distribution of stranded people after the earthquake.
. Any information published on this site will be valid in relation to Science Tokyo.



