Meteorites from Mars suffer a velocity boost due to the material pileup
Published: December 18, 2017
Researchers have performed numerical simulations to explore the launch mechanism of the Martian meteorites. According to the knowledge of shock physics, a strong shock compression higher than 50 GPa is required to accelerate martian materials up to the escape velocity of Mars (5 km/s). In contrast, detailed analysis of martian meteorites shows that they suffer only 30–50 GPa during the ejection. The researchers found that a material pileup in an excavation flow causes a significant velocity boost of materials near the surface without strong compression. This newly descovered "late-stage acceleration" could play an important role not only in the launch of martian meteorites, but also in the context of the (Litho-)Panspermia.
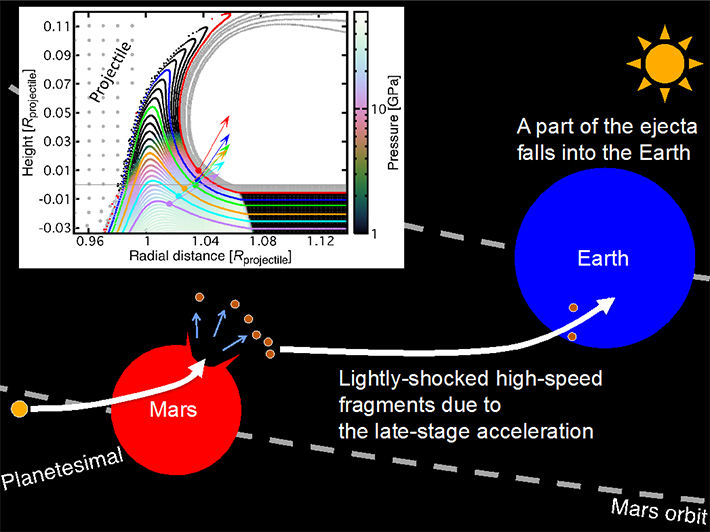
Figure 1. A cartoon on the generation of Martian meteorites.
The inset shows the figure shows the hydrodynamic behavior during a projectile penetration. The color bar indicates the temporal pressures of the data point. Selected six tracers with velocity vectors are indicated as filled circles. The tracer overlays at the same depth of the tracers are also shown. A material pileup is obvious, showing that the materials initially located at a deeper position (ex. Purple circle) extrude the surficial materials (ex. Red circle). The temporal pressure at the root of the ejecta curtain, where the late-stage acceleration occurs, reaches 10 GPa despite the height of the materials having already excessed ground level. The new finding suggests that the material transportation due to hypervelocity impacts, as illustrated here, occurs more easily than what was previously thought.
Background
One hundred and ninety-eight meteorites from Mars have been discovered on Earth as of Sep., 2017. Hypervelocity impacts on Mars have been a widely accepted mechanism that launches Martian rocks into the space. Petrographic analyses of the Martian meteorites have shown that they suffer relatively low peak pressure ranging from 30 to 50 GPa during impact ejection events. In contrast, shock physics tells us that a stronger shock compression higher than 50 GPa is required to accelerate materials up to the escape velocity of Mars (5 km/s). This contradiction between petrology and shock physics was the outstanding problem regarding the Martian meteorites' launch.
Methodology
The researchers numerically modeled a vertical impact onto the Martian surface using two independent hydrocodes (iSALE code and SPH code) to explore the launch mechanism of the Martian meteorites. The impact-driven pressure field and material movements near the impact point has been investigated in detail. The maximum spatial resolution in the computation employed in this study is one order of magnitude higher than that used in the previous studies.
Overview of Research Achievement
The research team found that a velocity boost of surficial materials occurs due to a material pileup in an impact-driven excavation flow without strong shock compression (See Figure 1). The newly discovered velocity boost mechanism has been named "late-stage acceleration". The parts of the ejecta mass that experienced 30–50 GPa and were ejected higher than 5 km/s were investigated. Although the mass is limited to 0.1–1 % of the projectile mass, this is sufficient for hypervelocity impacts to have been a plausible mechanism for the ejection of Martian meteorites.
Future Development
The new discovery of late-stage acceleration has a wide range of implications not only for the Martian meteorites' launch, but also for material exchange amongst planetary bodies (See Figure 1). Since microbes may survive the relatively weak shock compression, the late-stage acceleration could provide us with new insight into (Litho-)Panspermia. The researchers are planning to do a series of hypervelocity impact experiments to validate the numerically discovered new mechanism using a two-stage light gas gun installed at the Planetary Exploration Research Center, Chiba Institute of Technology, Japan.
Reference
Authors : |
Kosuke Kurosawa1 *, Takaya Okamoto1, Hidenori Genda2 |
Title of original paper : |
Hydrocode modeling of the spallation process during hypervelocity impacts: Implications for the ejection of Martian meteorites |
Journal : |
Icarus, 301, 219-234 |
DOI : |
|
Affiliations : |
1 Planetary Exploration Research Center (PERC), Chiba Institute of Technology
2 Earth-Life Science Institute (ELSI), Tokyo Institute of Technology
|
. Any information published on this site will be valid in relation to Science Tokyo.



