A research group based in a number of countries (Japan, Malaysia, Ukraine, and Germany), led by Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), have proposed an improved model for predicting the generation of thermal energy from nuclear fission processes, by focusing on Uranium-236. This model can help improve efficiency in nuclear power generation.
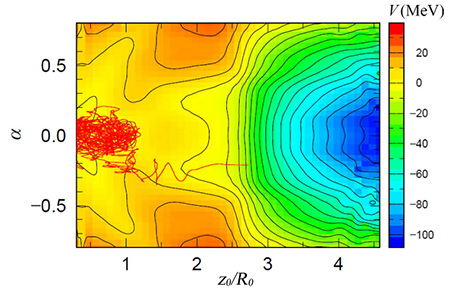
Figure 1. Energy trajectories in the 4D-Langevin model.
This color map represents the potential energy surface for U-236. The color changes as the excitation energy increases. Researchers used this net of energy relationships to account for the stochastic nature of the Langevin model and represent some key fluctuation–dissipation dynamics associated with Uranium scission points.
For all of us working with electricity, radioactive waste containment, or hospitals, controlling radioactive processes and predicting their behaviors are key to making our world function safely. Let's look at electricity generation for a quick example of how fission works. In order to run the turbines of atomic power stations that will eventually bring us our light and internet connections, nuclear power relies on a complicated interplay of atomic interactions, all initiated by the introduction of one neutron into an already stuffed nucleus. Scientists seek to understand how much thermal energy we can extract for the nuclear fission process, and work out what reaction products will be created. After nuclear fission has occurred, nuclei are broken up into smaller parts.
In our researchers' case, the generation of energy is observed from nuclear fission of Uranium-235 (U-235). As a neutron is bombarded into the U-235 nucleus, it produces a Uranium-236 (U-236) nucleus and gives it extra-energy to help it split into two separate fragments. The excitation energy causes the fragmentation, generating atomic energy (see Figure 1). However, predicting this energetic interaction is difficult, so scientists use simplified models to represent the fragmentation of the nucleus. The Langevin model represents the behavior of dynamic motion of a fissioning nucleus. Previously established Langevin models often considered three dimensions to describe the shape of the nuclei. These included a deformation factor, which describes the various geometries of the two nuclear fragments deformed as a result of fission.
Chikako Ishizuka and Satoshi Chiba at Tokyo Tech, leading this research group, have found that there is an additional factor that influences prediction within a Langevin model, while focusing on U-236. The team's fourth factor considers the deformation of the two separate fragments, rather than assuming the two fragments have the same deformation factor.
Unlike previous 3D Langevin models, the researchers have enhanced the Langevin model to four dimensions so that it can consider the thermal energy of nuclear fragments and consider the individual shape of the fission fragments by taking into account that the heavy and light elements of the fragments behave differently. The results appear to fit empirical data of nuclear fission better than previously established models. Especially no theoretical models have not reproduced the kinetic energy i.e. the thermal energy of nuclear fission, with predictive power. As seen in Figure 2, the resulting kinetic energy data of the 4D model fits well with observed measurements, in comparison with previous models (shown with the purple and green symbols) without special assumptions.
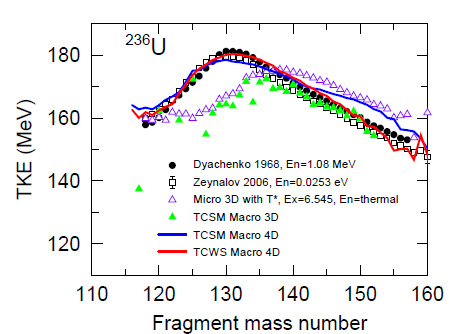
Figure 2. Comparison of TKE (Total Kinetic Energy) distributions
Note the close match between the results of TCWS 4D (the new model discussed here) and the observed empirical results by Dyachenko et al. and Zeynalov et al.
The Langevin 4D model improves how we can predict low-energy fission and can be used for various nuclei such as poisonous nuclear wastes populated by successively absorbed neutrons starting from uranium. The authors of this work are continuing to develop new applications, with particular emphasis on a future 5D dynamical model that will improve predictive accuracy even further.
Reference
Authors : |
Chikako Ishizuka1, ∗, Mark D. Usang1, 2, Fedir A. Ivanyuk1, 3, Joachim A. Maruhn4, Katsuhisa Nishio5, and Satoshi Chiba1, 6 |
Title of original paper : |
Four-dimensional Langevin approach to low-energy nuclear fission of 236U |
Journal : |
Physical Review C |
DOI : |
|
Affiliations : |
1Laboratory for Advanced Nuclear Energy, Institute of Innovative Research,
Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo 152-8550, Japan
2Malaysian Nuclear Agency, Bangi 43000, Malaysia
3Institute for Nuclear Research, Kiev 03028, Ukraine
4Institute for Theoretical Physics, Goethe University, Frankfurt am Main 60323, Germany
5Advanced Science Research Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Tokai, Ibaraki 319-1195, Japan
6National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, Tokyo 181-8588, Japan
|
. Any information published on this site will be valid in relation to Science Tokyo.




