The new cell-free protein crystallization (CFPC) method developed by Tokyo Tech includes direct protein crystallization and is a major headway in the field of structural biology. This technique will enable the analysis of unstable proteins that could not be studied using conventional methods. Analyzing these will increase our knowledge of cellular processes and functions.
While we are familiar with certain crystals like salt and sugar that we use in our everyday life, there is another set of crystals, hidden from the naked eye, that is crucial to our biology. Microscopic protein crystals are found in living cells and help sustain processes like immune system activation, protein storage, and protection.
To better understand the relationship between protein crystals' structure and function, scientists developed the in-cell protein crystallization (ICPC) method, which can directly observe protein crystals in living cells, ensuring high-quality crystals without the need for purification processes or complex screening methods. However, despite its many advantages, very few structures were reported because the crystals formed in living cells didn't have the size and quality that was required for analysis. So, a team of researchers from Japan, led by Prof. Takafumi Ueno of Tokyo Tech aimed to develop a better method. And recently, they hit a breakthrough!
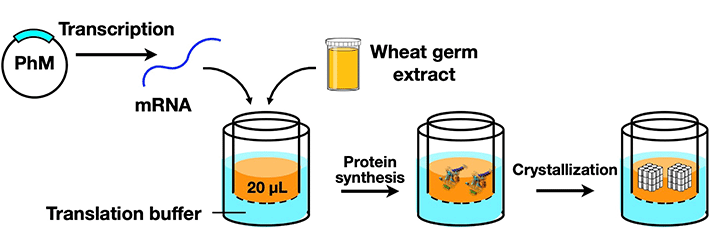
In their article published in Scientific Reports , the team reported the development of a technique that would make protein crystallization and analysis more efficient and effective. This technique—a cell-free protein crystallization (CFPC) method—was a hybrid between in vitro protein crystallization and ICPC, and allowed rapid and direct formation of protein crystals without the need for complicated crystallization and purification methods.
"ICPC is expected to become an important tool in crystal structure analysis but we need a method to obtain better resolution protein crystal structures. So, we focused on establishing high-quality protein crystallization using CFPC with small-scale and rapid reactions," says Prof. Ueno, who also heads the Ueno Laboratory at Tokyo Tech. Members of this lab study naturally-occuring protein assemblies, their structure, and functions, aiming to apply this knowledge to develop innovative biotechnology and energy solutions.
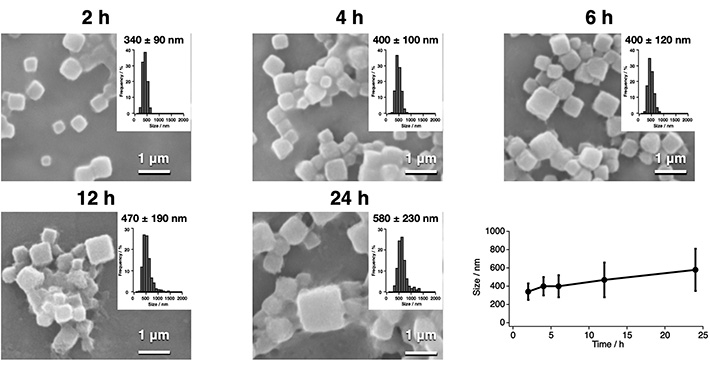
Coming back to the team conducting the current study (some of whom are also members of the Ueno Laboratory), they used a wheat germ protein synthesis kit, which is a tool for the synthesis of polyhedrin monomer, a viral protein produced in insect cells by cypovirus infection. This protein was then crystallized using the new CFPC method, leading to the formation of nano-sized polyhedra crystals (PhCs). The team could efficiently complete this process within 6 hours, using only 20 microlitres of the reaction mixture. Scanning electron microscopy images indicated that the PhCs had excellent purity, which allowed the determination of their structure at a resolution as high as 1.95 Å (or 1.95 Angstrom). To further explore the capabilities of their new system, the team carried out the structural analysis of crystalline inclusion protein A (CipA). Its structure was determined at a high resolution of 2.11 Å, something that had never been reported before this study.
. Any information published on this site will be valid in relation to Science Tokyo.