Discovery of new ferroelectric silicate materials
Published: February 16, 2015
Barium titanate (BaTiO3) and lead zirconium titanate (Pb(Zr,Ti)O3) are well known ferroelectric materials that are used for fabricating capacitors and actuators. Their crystal structures belong to the perovskite-type oxide group (ABO3) with a BO6 octahedral coordination.
However, new and important ferroelectric compounds with other structural groups have not been found during the last decade.
Now, Mitsuru Itoh and Hiroki Taniguchi (present address:Nagoya University) and their colleagues have succeeded in the synthesis of new ferroelectric silicates with a tetrahedral coordination. The mechanism for the evolution of ferroelectricity was studied by both experiments and theoretical calculations.
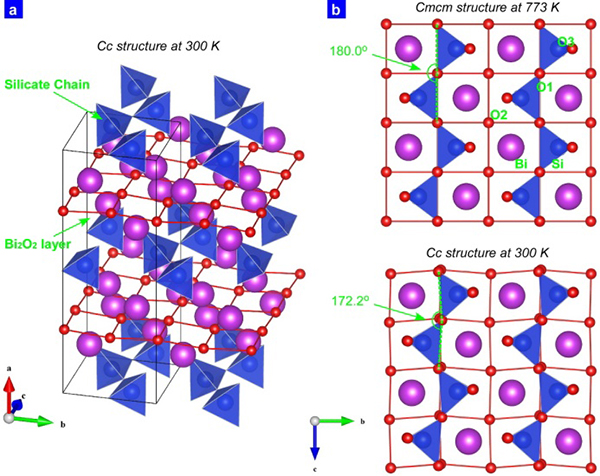
Single crystalline Bi2SiO5 was fabricated by a melting and solidification process via an intermediate glassy state. Dielectric measurements, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray structural analysis, transmission electron microscopy, and first principle calculations were conducted for single crystals.
The refined crystal structure and calculated electronic and phonon structures consistently explained the ferroelectricity of this material appearing below 673 K.
The origin of ferroelectricity of Bi2SiO5 was attributed to the twisting of the silicate tetrahedral chains. This new finding may trigger materials research of new ferroelectrics with other structural groups and coordination numbers of 4, 5, and 7.
Reference
Authors: |
Hiroki Taniguchi, Akihide Kuwabara, Jungeun Kim, Younghun Kim, Hiroki Moriwake, Sungwng Kim, Takuya Hoshiyama, Tsukasa Koyama, Shigeo Mori, Masaki Takata, Hideo Hosono, Yoshiyuki Inaguma, and Mitsuru Itoh. |
Title of original paper: |
Ferroelectricity Driven by Twisting of Silicate Tetrahedral Chains. |
Journal, volume, pages and year: |
Angewandte Chemie International Edition 52, 8088 (2013). |
Digital Object Identifier (DOI): |
|
Affiliations: |
Materials and Structures Laboratory, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan Fine Ceramics Center, Department of Advanced Materials Science, The University of Tokyo, Department of Materials Science, Osaka prefectural University, Department of Chemistry, Gakushuin University |
. Any information published on this site will be valid in relation to Science Tokyo.