The molecular mechanism underlying enzyme activity regulation of ubiquitin-specific protease 8 (USP8) has been decoded by researchers at Tokyo Tech. USP8 has been implicated in Cushing's disease pathogenesis. They identified an autoinhibitory region on the enzyme that interacts with its catalytic region. They also provide first evidence on the release of autoinhibition due to USP8 mutations as the underlying cause behind Cushing's disease. Their findings could be invaluable for understanding Cushing's disease pathogenesis.
Cushing's disease, caused by an excess of the steroid hormone cortisol in the body (Figure 1), affects thousands of people worldwide and has been the subject of extensive medical research. Developing targeted therapy to treat Cushing's disease would require a thorough understanding of its underlying molecular mechanisms. At the molecular level, mutations of ubiquitin-specific protease 8 (USP8), a deubiquitinating enzyme that cleaves ubiquitin from proteins, have been implicated in Cushing's disease pathogenesis.
![Figure 1 Signs and symptoms of Cushing's disease Mutations of the enzyme ubiquitin-specific protease 8 (USP8) in pituitary adenoma cause excess secretion of the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) that stimulates cortisol production—the hallmark of Cushing's disease. This affects major organs and tissues in the body, and can have serious complications if left untreated. Little is known about the details of the effects of these mutations on USP8 function. Researchers from Tokyo Tech in Japan have now implicated the dysregulation of USP8 in Cushing’s disease pathogenesis. Copyright: [designua] © 123RF.com](/english/news/img/news-28831-01.png)
Figure 1. Signs and symptoms of Cushing's disease
Mutations of the enzyme ubiquitin-specific protease 8 (USP8) in pituitary adenoma cause excess secretion of the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) that stimulates cortisol production—the hallmark of Cushing's disease. This affects major organs and tissues in the body, and can have serious complications if left untreated. Little is known about the details of the effects of these mutations on USP8 function. Researchers from Tokyo Tech in Japan have now implicated the dysregulation of USP8 in Cushing’s disease pathogenesis. Copyright: [designua] © 123RF.com
Typically, USP8 binds to a class of adaptor proteins called 14-3-3 to undergo inhibition. Mutations of USP8 in Cushing's disease abolish this binding of USP8 to 14-3-3, which leads to excess secretion of the adrenocorticotropic hormone that stimulates cortisol production—the hallmark of Cushing's disease. However, little is known about the details of the effects of these mutations on USP8 function.
So, a group of researchers from Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) deep dived into the molecular makeup and workings of USP8 in hopes of finding therapeutic targets against Cushing's disease. Explaining the motivation behind their study, Dr. Toshiaki Fukushima, Assistant Professor at Cell Biology Center, Institute of Innovative Research at Tokyo Tech, who led the study, says, "We were already exploring the role of mutated USP8 in Cushing’s disease. Understanding the effects of mutations on its activity regulation was naturally the next step in our research."
The researchers found that wildtype USP8 possesses a unique amino acid region from position 645 to 684 within its 1118-residue-long amino acid sequence, which had autoinhibitory properties (Figure 2). This region was found to form a WW-like domain structure. To explore further, they carried out biochemical analyses, including fluorescence resonance energy transfer measurement, and docking simulations in silico, and observed that the WW-like domain binds to the catalytic domain of USP8 to narrow the entrance to the ubiquitin-binding pocket that forms an essential site in USP8's deubiquitinating reaction.
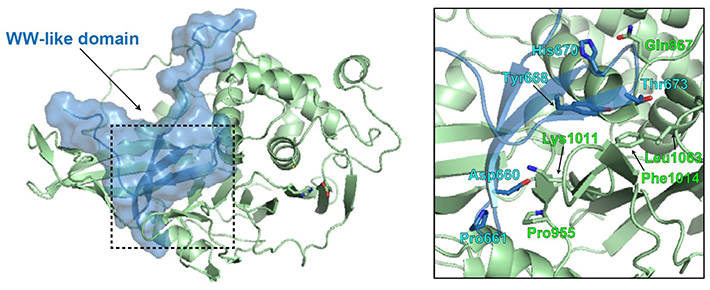
Figure 2. Structural modeling of the WW-like autoinhibitory domain on USP8
Researchers from Tokyo Tech have identified a WW-like autoinhibitory domain in USP8. The WW-like domain (blue) appears to occupy the ubiquitin-binding pocket of the catalytic domain (green), to facilitate enzymatic inhibition.
Next, the researchers found that USP8 activity inhibition mediated through 14-3-3 proteins was in part achieved by enhancing the interaction between the WW-like domain and the catalytic domain. Further, they analyzed the effects of pathogenic mutations of USP8. The mutations were found to abolish the binding of USP8 to 14-3-3, as observed by the researchers in their previous experiment, suppressed the interaction between the WW-like and catalytic domains, and led to the exacerbation of the deubiquitinating activity of USP8 (Figure 3).
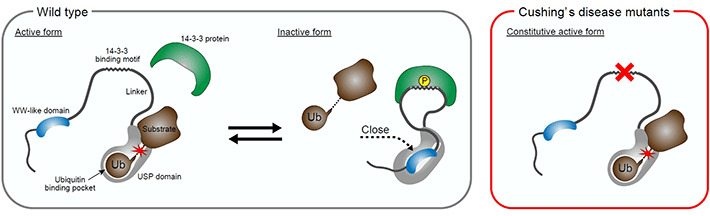
Figure 3. Cushing's disease-associated mutations of USP8 release the autoinhibition of USP8
Wildtype USP8 activity is regulated by the adaptor protein 14-3-3. 14-3-3 inhibits USP8 in part through the enhancement of the interaction of the WW-like domain and the catalytic domain (USP domain in the figure). The mutation hotspot in Cushing's disease is located on the 14-3-3-binding motif in USP8. The mutations render USP8 unable to bind to 14-3-3, which, in turn, suppresses the interaction of the WW-like and catalytic domains, causing constitutive activation of USP8 and Cushing's disease pathogenesis.
These findings have been published as a research article in Communications Biology.
Overall, the researchers appear to have deciphered what constitutes the regulation of USP8 enzyme activity and how it is dysregulated in Cushing's disease. Whether hyperactivated USP8 would serve as a therapeutic target for Cushing's disease warrants further research. In this regard, Dr. Fukushima hopes, "Our study regarding USP8 is perhaps a stepping-stone to developing targeted therapy against Cushing’s disease. Besides developing on our novel findings, we hope that our work will inspire similar research as well."
The insights offered by this study promise hope for medical researchers and patients with Cushing's disease alike.
Reference
Authors : |
Keijun Kakihara1,2, Kengo Asamizu1, Kei Moritsugu3, Masahide Kubo1, Tetsuya Kitaguchi4, Akinori Endo2, Akinori Kidera3, Mitsunori Ikeguchi3, Akira Kato1, Masayuki Komada1,2 , and Toshiaki Fukushima1,2 |
Title of original paper : |
Molecular basis of ubiquitin-specific protease 8 autoinhibition by the WW-like domain |
Journal : |
Communications Biology |
DOI : |
|
Affiliations : |
1 School of Life Science and Technology, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama, Japan
2 Cell Biology Center, Institute of Innovative Research, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama, Japan
3 Graduate School of Medical Life Science, Yokohama City University, Yokohama, Japan
4 Laboratory for Chemistry and Life Science, Institute of Innovative Research, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama, Japan
|
. Any information published on this site will be valid in relation to Science Tokyo.


![Figure 1 Signs and symptoms of Cushing's disease Mutations of the enzyme ubiquitin-specific protease 8 (USP8) in pituitary adenoma cause excess secretion of the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) that stimulates cortisol production—the hallmark of Cushing's disease. This affects major organs and tissues in the body, and can have serious complications if left untreated. Little is known about the details of the effects of these mutations on USP8 function. Researchers from Tokyo Tech in Japan have now implicated the dysregulation of USP8 in Cushing’s disease pathogenesis. Copyright: [designua] © 123RF.com](/english/news/img/news-28831-01.png)